How PPA Reduces Melt Fracture and Sharkskin Defects in Extrusion Processes
In high-speed polymer extrusion, surface defects like melt fracture and sharkskin are not just cosmetic issues—they directly affect product performance, customer acceptance, production efficiency, and profitability. For manufacturers producing blown films, cast films, pipes, cables, and profiles, these defects can lead to rejections, customer complaints, downtime, and higher conversion costs.
One of the most effective industrial solutions to eliminate these defects is the use of PPA (Polymer Processing Aid). PPA additives have become a critical tool for polymer converters who want to run extrusion lines faster while maintaining consistent surface quality.
This blog explores, in technical depth, how PPA works, why melt fracture occurs, and how PPA helps B2B processors achieve higher output with better surface finish.
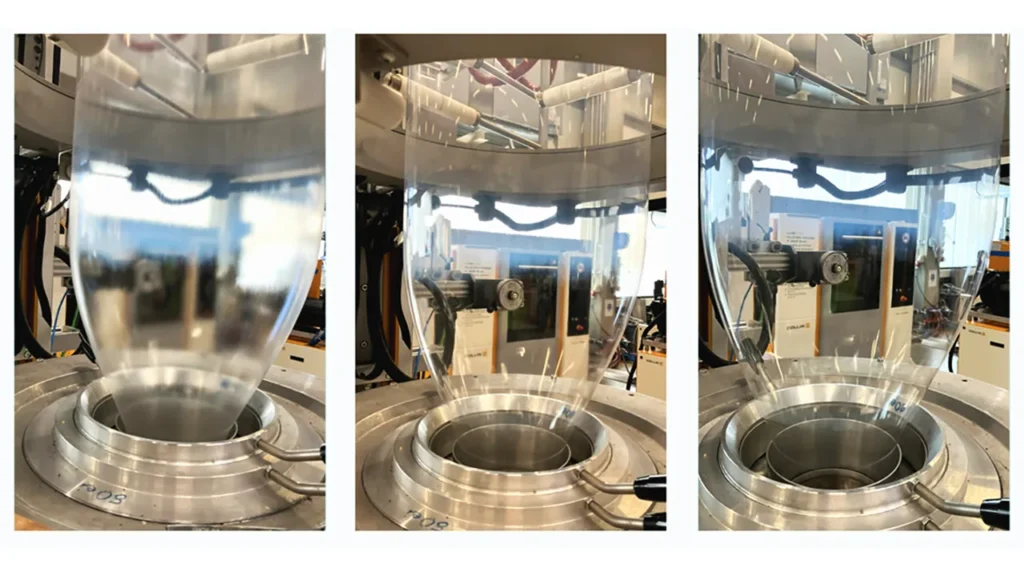

What is Melt Fracture and Sharkskin in Polymer Extrusion?
During extrusion, molten polymer is pushed through a die under high pressure. Ideally, the polymer should flow smoothly, producing a uniform surface. However, at higher throughput rates, flow instabilities occur at the die exit, resulting in visible surface defects.
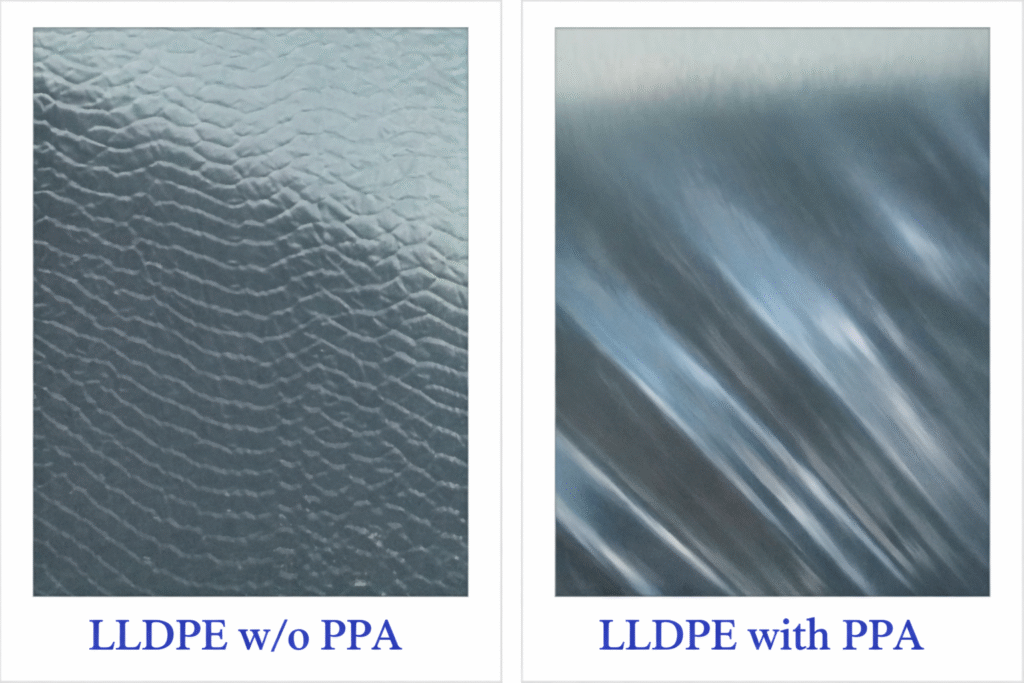
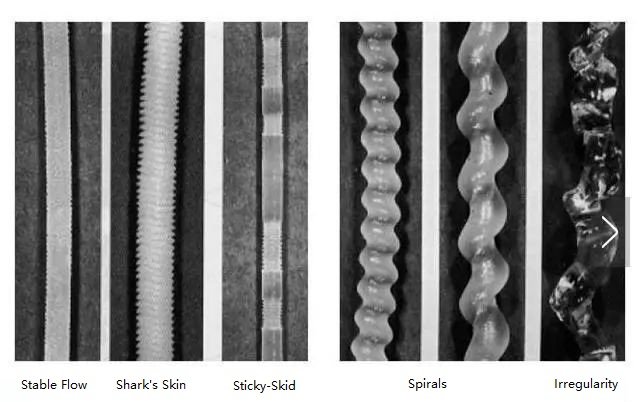
1. Sharkskin Defect
Sharkskin is a fine, repetitive surface roughness that appears like the skin texture of a shark. It typically occurs at moderate shear stress levels and is common in:
LLDPE blown film
HDPE film extrusion
PP cast film
Cable insulation extrusion
Root cause:
Sharkskin occurs due to high shear stress at the die lip, where the polymer experiences sudden acceleration as it exits the die. This creates a stress imbalance, leading to micro-cracks on the surface.
2. Melt Fracture Defect
Melt fracture is a more severe extrusion defect where the surface becomes:
distorted
wavy
rough
cracked
sometimes completely irregular
It usually occurs at higher shear rates compared to sharkskin.
Root cause:
Melt fracture occurs when the polymer flow transitions from stable to unstable due to excessive elastic stress buildup in the melt. When this stress exceeds the polymer’s ability to relax, the melt breaks in an irregular manner.
Why Do Melt Fracture and Sharkskin Defects Happen?
The key technical driver behind these defects is die wall shear stress.
Important Parameters that Trigger Melt Fracture
Higher extrusion speed (higher throughput)
Higher melt elasticity (LLDPE, metallocene PE, PP)
Narrow die gap
Higher melt temperature variation
Poor die design or worn die lips
Higher molecular weight polymers
High friction between polymer melt and die surface
What is PPA (Polymer Processing Aid)?
PPA (Polymer Processing Aid) is a specialized additive—typically fluoropolymer-based or silicone-based—used in small dosages to improve polymer melt flow behavior during extrusion.
PPA is commonly supplied in the form of a masterbatch compatible with:
LLDPE
LDPE
HDPE
PP
Typical dosage: 200 ppm to 2000 ppm, depending on resin type and processing conditions.
How PPA Reduces Melt Fracture and Sharkskin Defects (Technical Explanation)
The working mechanism of PPA is extremely interesting and is based on reducing wall slip resistance inside the extrusion die.
1. PPA Promotes Wall Slip and Reduces Die Shear Stress
In normal extrusion, molten polymer adheres to the die wall, meaning the velocity of polymer at the wall is nearly zero. This creates a strong velocity gradient, leading to high shear stress.
Without PPA
Polymer sticks to die surface
High friction at die wall
Shear stress increases rapidly
Sharkskin appears first
Melt fracture occurs at higher speeds
With PPA
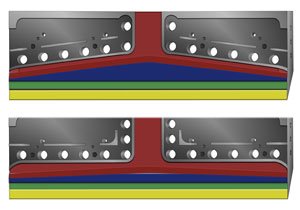
PPA migrates to the die wall and forms a thin lubricating layer.
This layer causes controlled wall slip, meaning polymer begins sliding over the die surface instead of sticking.
Result:
Reduced die wall shear stress
Stable flow at higher throughput
Smooth film surface
2. PPA Forms a Low-Friction Coating on Die Surface
One of the most proven mechanisms of fluoropolymer-based PPA is that it deposits a microscopic coating on the metal die surface.
This coating behaves like a die conditioner, reducing metal-polymer friction.
Key benefits:
Improved polymer flow uniformity
Reduced melt tearing at die exit
Lower risk of surface cracking
In industrial extrusion, this is referred to as die surface modification, and it is one of the primary reasons PPA is so effective for film extrusion lines.
3. PPA Reduces Melt Elastic Stress Buildup
Polymers like LLDPE and metallocene LLDPE have high elasticity. At high shear, the polymer chains stretch and store elastic energy.
When exiting the die, this energy is released abruptly, causing instability at the die lip, leading to sharkskin.
PPA reduces the friction-driven stress buildup, allowing polymer chains to relax more smoothly.
Result:
Less surface tearing
Reduced elastic recoil
Better surface uniformity
4. PPA Helps Achieve Stable Extrusion at Higher Output Rates
For most extrusion plants, the goal is clear:
Higher output + stable surface quality = higher profitability
By lowering shear stress and promoting slip, PPA allows processors to increase throughput without crossing the critical shear stress limit.
What processors typically observe after adding PPA:
Ability to increase extrusion speed by 5%–25%
Higher production per hour
Lower scrap generation
More stable bubble in blown film
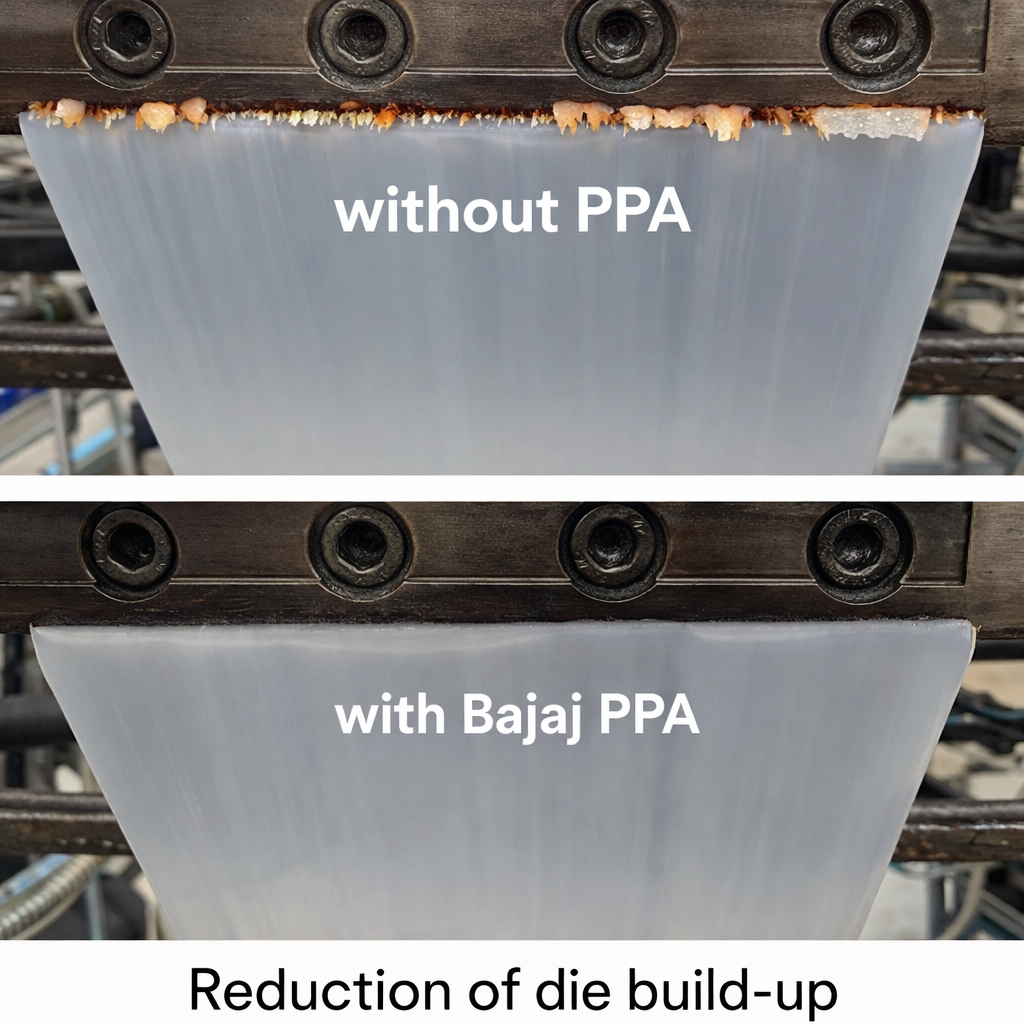
5. PPA Minimizes Die Build-Up and Reduces Frequent Cleaning
Another major operational issue is die build-up, also called die drool. This occurs when degraded polymer, additives, or fillers deposit near the die lips.
PPA reduces stagnation and polymer hang-up zones by improving slip behavior.
Result:
Less die drool
Longer production cycles
Reduced shutdown time for cleaning
Improved quality consistency over long runs
How Fast Does PPA Work? (Purge Time and Activation)
Many purchase managers ask:
“If we add PPA today, when will sharkskin disappear?”
The answer depends on how quickly the die surface becomes coated.
Typical PPA Activation Time:
15 to 60 minutes in most film lines
Faster in higher shear extrusion
Longer if old deposits exist inside die
Some processors use a higher initial dosage (shock dose) and then reduce to a maintenance dosage.
Example:
Initial: 1500 ppm for 30 minutes
Maintenance: 500 ppm continuous

PPA Dosage for Melt Fracture and Sharkskin Control
Dosage depends on resin type, melt index, die design, and line speed.
General Recommended Range:
| Application | Typical PPA Dosage |
|---|---|
| Blown film (LLDPE/LDPE) | 300–1500 ppm |
| Cast film | 200–1000 ppm |
| Pipe extrusion | 500–2000 ppm |
| Cable extrusion | 300–1500 ppm |
| Metallocene polymers | 800–2000 ppm |
For B2B buyers, dosage optimization is crucial because PPA is a performance additive—small dosage variations can impact output and cost.
Which Polymers Benefit the Most from PPA?
PPA is most effective in extrusion grades that show strong melt elasticity or high friction at die wall.
High Benefit Polymers:
LLDPE
mLLDPE
HDPE
PP
Especially in metallocene LLDPE, sharkskin is a frequent issue due to high elasticity. PPA becomes almost essential to achieve smooth film surface at high output.

Common Industrial Applications of PPA in Extrusion
PPA is widely used in:
Blown Film
Packaging film
Stretch film
Agricultural mulch film
Lamination film
Pipe and Profile Extrusion
HDPE pipes
PE profiles
Water pipe extrusion
Wire and Cable
Insulation extrusion
Jacketing compounds
Sheet and Cast Film
Thermoforming sheets
PP/PE sheets

Blown Film
Die Drool & Deposits ,Clean Die , Stable Output
Key Benefits of PPA for B2B Plastic Processors
From a commercial and technical standpoint, PPA provides measurable benefits:
1. Improved Surface Finish
Eliminates sharkskin
Minimizes melt fracture
Produces glossy film
2. Increased Output and Productivity
Allows higher extrusion speed
Reduces downtime
3. Lower Scrap and Rejection Rate
Better film aesthetics
Better printability and lamination
4. Better Gauge Uniformity in Film
More stable melt flow
Reduced flow instabilities
5. Reduced Die Build-Up
Less die drool
Longer continuous production
How to Select the Right PPA Masterbatch?
For purchase managers and technical buyers, selecting PPA should not be based only on price per kg. It should be evaluated based on performance per ppm.
Key Parameters to Evaluate:
Compatibility with polymer (PE/PP)
Dispersion quality
Thermal stability
Migration performance
Regulatory compliance (FDA, EU if needed)
Impact on haze and transparency
No negative effect on sealing or printing
Important Note: PPA vs Lubricants (They Are Not the Same)
Many extrusion plants confuse PPA with internal lubricants like waxes or stearates.
Lubricants:
Work inside polymer melt
Reduce internal friction
Can affect sealing strength and bonding
PPA:
Works at die wall surface
Reduces metal-polymer friction
Improves extrusion stability
So for sharkskin and melt fracture, PPA is far more effective than standard lubricants.
Does PPA Affect Film Properties?
At correct dosage, PPA typically has negligible impact on:
tensile strength
elongation
sealing performance
haze/gloss (often improves gloss)
However, overdose may lead to:
slight surface slip issues
printing challenges in rare cases
additive blooming if not formulated properly
That’s why technical dosage optimization is important for industrial extrusion.
Why Purchase Managers Prefer PPA as a Cost-Saving Solution
Even though PPA masterbatch is a premium additive, it reduces total cost by:
reducing scrap
increasing line output
reducing die cleaning time
improving customer acceptance rate
improving long-run production stability
Example Business Impact:
If a blown film line increases output by even 10%, the payback from PPA usage becomes extremely high compared to its dosage cost.
Conclusion: PPA is a Powerful Solution for Melt Fracture and Sharkskin Control
Melt fracture and sharkskin defects are direct results of high die wall shear stress and unstable polymer flow. PPA solves these challenges through a scientifically proven mechanism:
- Die wall lubrication
- Controlled wall slip
- Reduced shear stress
- Stable flow at higher output
- Reduced die build-up
For extrusion processors and B2B decision-makers, PPA is not just an additive—it is a productivity enhancer and a quality assurance tool.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. Can PPA eliminate sharkskin completely?
Yes, in most PE and PP extrusion applications, PPA can completely remove sharkskin when the correct dosage is used.
2. Does PPA work for both LLDPE and HDPE?
Yes. PPA is widely used in LLDPE and HDPE blown film, pipe, and cable extrusion.
3. How long does PPA take to show results?
Typically 15–60 minutes depending on extrusion conditions and die cleanliness.
4. Is PPA required for metallocene LLDPE?
In many cases, yes—because metallocene polymers are more prone to sharkskin due to higher melt elasticity.
About Bajaj Plast Pvt. Ltd.
Bajaj Plast Pvt. Ltd. is a leading manufacturer of high-quality masterbatch solutions, dedicated to innovation, sustainability, and excellence. With a strong focus on customer satisfaction and cutting-edge technology, we are committed to delivering superior products that meet the evolving needs of the polymer industry.



