HDPE Monofilament Yarn
Mono filaments are single threadlike synthetic fibers made of HDPE , PP , Nylon , etc. Monofilament extrusion is a process used to make continuous strands of polymeric material for a variety of consumer and industrial products. Both one and two polymer systems called co-extrusion or bi component extrusion are widely used. Mono filament yarns are usually circular and solid in cross section.
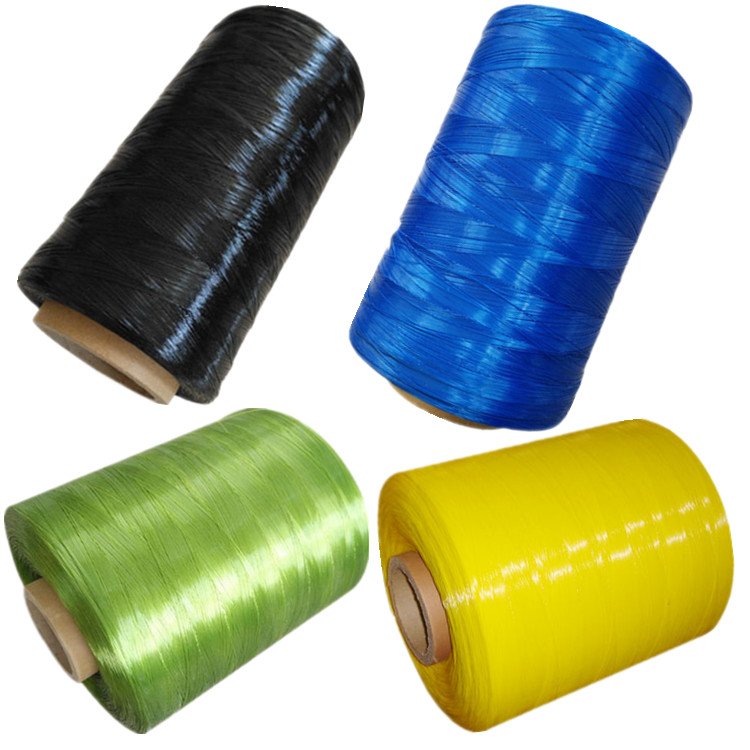


The shape of the filament can be altered to produce non circular and/or hollow filaments. The diameter range of mono filament yarns varies between 100–2000 μm. The apparel applications of mono filaments are limited owing to their low bulk and high bending rigidity. The examples of mono filaments
read more
from everyday life include fishing line, dental floss, in sports racquets, bristles of tooth brushes, insect nets, agricultural tent houses, fencing wires, etc. Hollow mono filaments are used in softer sewing thread applications where elastomeric mono filaments find applications in pressure garments.
Mono filament fabrics are woven from extruded synthetic filaments produced in diameters from 30μm to 3mm. These fabrics have become important as filter used in a broad range of industries and applications. Generally, HDPE Mono filament Yarns are
read more
materials that are used for weaving braiding and twisting applications in agro, geo and industrial textiles. It has high Tenacity, Chemical Resistance and Flexibility. Yarn Thickness varies between 0.1mm to 0.7mm (70dr to 3300dr).

Applications of HDPE Monofilament Yarns
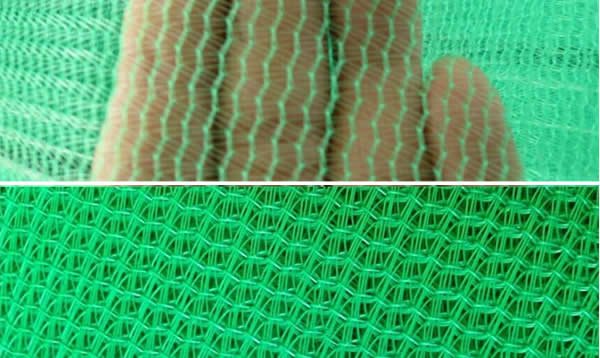
Weaving material for agro textiles such as filters, shade nets, industrial textiles & furnishing fabrics.

Braiding material for ropes, fishing nets, fences, rubber bands and strings

Knitting and twisting into safety nets, protection covers, open packaging, & marking materials

Reinforcement material for coating products.
Why Bajaj ?

Unique features
Trouble shooting guide - HDPE Monofilaments
| PROBLEM | POSSIBLE CAUSES | SOLUTIONS |
|---|---|---|
| Frequent filament breakage at quench bath | Moisture in the material | Use hopper dryer. |
| Contamination in the material | Inspet feed, reduce or stop using recycled material | |
| Surging in extruder | Run at higher pressure or with better mixing screw, analyse period of surging and relate to drive controllers. | |
| Breakage of particular filaments due to partially blocked holes of extrusion die / spinneret. | Clean the die holes for blockage, reduce extrusion temperature if at higher side, check for uneven temperature or material distribution in the extrusion die head which can cause uneven melt flow pattern | |
| Oxidation & weakening of filament surface | Run at lower temperature or reduce the distance between die head & quench bath. | |
| Melt draw down ratio too high | Reduce melt draw-down ratio | |
| Quench bath temperature too low | Increase quench bath temperature to desired level. | |
| Molten filaments sticking to each other | Separate the filaments properly after quenching. | |
| Melt too cold which reduces ductility. | Increase melt temperature | |
| Frequent filament breakage at stretching oven | Higher stretch ratio, low stretching temperature. | Optimize stretching parameters, both of these produce excessive tension in the filaments. |
| Stretching temperature too high. | Reduce stretch temperature, if it’s too high it will draw the filaments but without orientation causing filament breaks under normal stretching tension. | |
| Abrasive marks or scratches on godet rolls. | Grind them smooth or wrap them with Teflon tapes | |
| Jerks & erratic drive of the godet rolls. | Check smoothness of operation for all moving parts. | |
| Non-uniformity of filaments | Contaminated polymer melt | Inspect feed, reduce or stop using recycled material. |
| Non-uniform dispersion of pigments in polymer melt | Use good quality pigments, preferably use base polymer of masterbatch compatible / same as parent material. | |
| Surging in extruder | Run at higher pressure or with better mixing screw , check production rate & reduce if running at higher production rate than recommended. | |
| Through-put variation | Check metering pump drive for variation RPM check for agglomerate formation at feed zone. | |
| Broken or cracked filter pack | Change filter pack, broken filter pack causes uneven melt flow to extrusion die / spinneret. | |
| Temperature variation at extrusion die | Check for actual & set temperature, check for burnt out heaters. | |
| Check for actual & set temperature, check for burnt out heaters. | Maintain quench water temperature at desired level. | |
| Variation in godet speed | Check godet drive for speed variation , jerks. | |
| Jerks & insufficient pressure on nip rolls. | Check and adjust pressure on nip rolls. | |
| Poor Surface appearance | Moisture in the material, master batch or pigments. | Use hopper dryer at feed section. |
| Degradation of material in extruder. Melt fracture. | Reduce extrusion temperature. | |
| Melt fracture | Reduce extrusion rate, line speed, use larger dia extrusion hole with the higher melt draw down ratio, reduce entrance angle in die holes, increase extrusion temperature. | |
| Lower tenacity | Lower stretching temperature | Increase stretching temperature |
| Lower molecular orientation | Increase stretch ratio, optimise stretching temperature, too high or too low stretching temperature reduce filament tenacity, note that changes of orientation may also change the filament diameter, requiring compensating adjustment elsewhere to maintain desired filament diameter. | |
| Nicks & cuts in filaments All causes related to non-uniformity of filaments. | Examine broken & unbroken filaments, look for a repetitive pattern & source of defect generation. |


