Masterbatch Quality Parameters Every Purchase Manager Must Check
(Technical Guide for Smart Procurement)
In the plastics industry, masterbatch is not just an additive—it is a critical raw material that directly influences product appearance, processing stability, mechanical performance, rejection rate, and final customer satisfaction.
For purchase managers, selecting masterbatch based only on price per kg is a risky strategy. A cheaper masterbatch can cause poor dispersion, shade variation, processing downtime, filter choking, extrusion instability, and high scrap generation, ultimately increasing total production cost.
This technical guide explains the most important masterbatch quality parameters every procurement professional must verify before finalizing any supplier.
Why Quality Parameters Matter More Than Price
Many purchase decisions fail because procurement teams focus only on:
Cost per kg
Shade card approval
Supplier promises
But the real performance of masterbatch is determined by its:
dispersion quality
pigment concentration consistency
thermal stability
compatibility with base polymer
processing cleanliness
A masterbatch that saves ₹10/kg but increases rejection by 2% can cost lakhs in losses.

Top Masterbatch Quality Parameters Every Purchase Manager Must Check
1. Pigment / Additive Loading Percentage (Active Content)
One of the most important masterbatch parameters is active ingredient percentage, commonly called loading.
What to Check:
Pigment content (%)
Additive content (%)
Standard deviation across batches
Why It Matters:
If loading fluctuates, your production will face:
Shade inconsistency
Variable dosing requirement
Overconsumption of masterbatch
Higher production cost per kg of finished product
Ideal Expectation:
A professional supplier maintains:
±0.5% batch-to-batch loading variation for high-end applications.

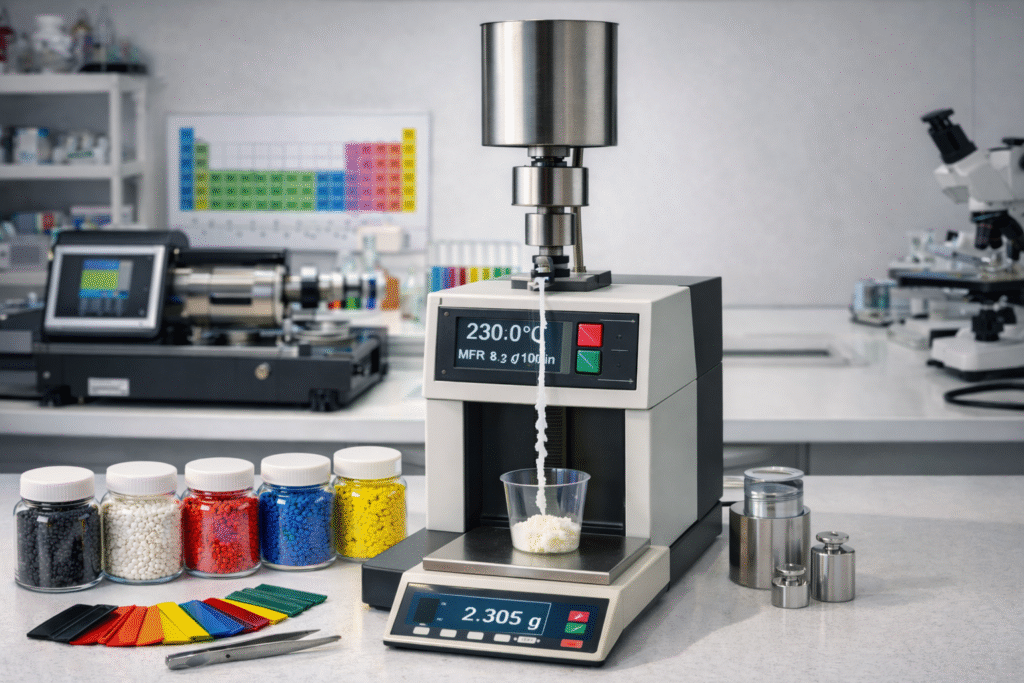
2. Melt Flow Index (MFI) of Masterbatch
MFI is a key indicator of flow behavior and processing compatibility.
What to Check:
Masterbatch MFI @ standard test conditions
Compare with base polymer MFI
Why It Matters:
If masterbatch MFI is too low compared to polymer:
poor mixing
high torque load
improper dispersion
streaking and specks
If masterbatch MFI is too high:
polymer viscosity imbalance
weak mechanical properties
film breakage risk
Recommended Practice:
Procurement must ensure masterbatch MFI is within acceptable processing range.
Example:
For LDPE film extrusion base polymer MFI 2.0, masterbatch should ideally be between 2 to 8 depending on pigment type.

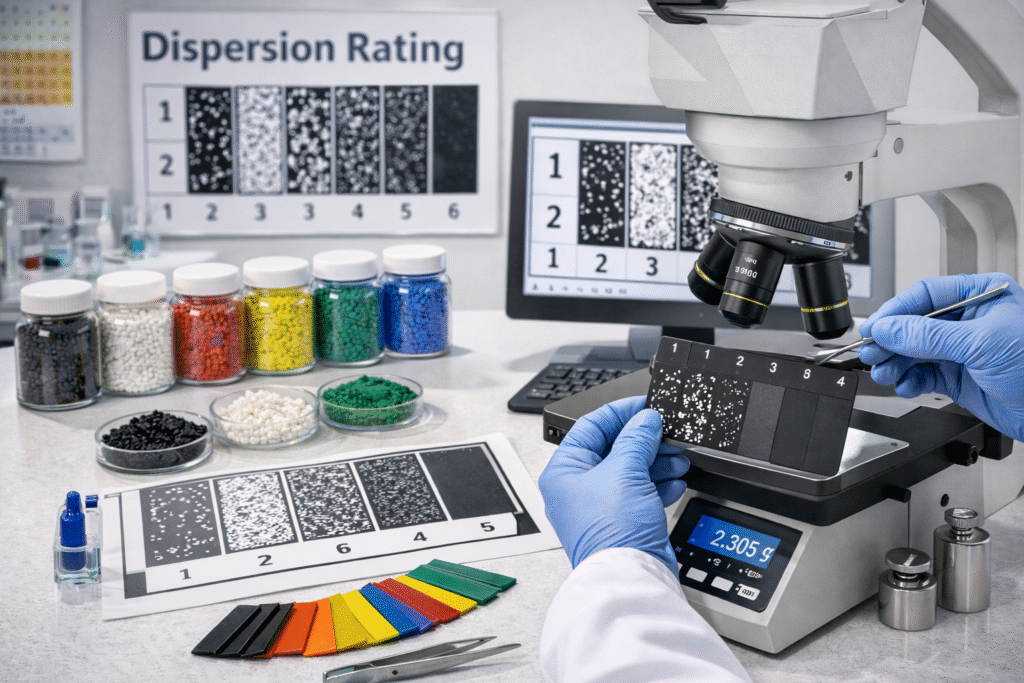
3. Dispersion Rating (Most Critical for Film & Molding Applications)
Dispersion is the ability of pigment/additive particles to spread uniformly in the polymer matrix.
What to Check:
Dispersion test report
Microscopic evaluation (DIN / ISO)
Filter mesh residue test
Why It Matters:
Poor dispersion causes:
black spots
color streaking
surface roughness
die lines in film
weak mechanical strength
Technical Standards:
Dispersion is typically evaluated by:
DIN 55986
ISO 18553
Microscopic dispersion grading
Purchase Tip:
Ask supplier for dispersion grading report such as:
Grade 1 (Excellent)
Grade 2 (Good)
Grade 3 (Average)
Grade 4 (Reject)
For premium B2B supply chain, Grade 1 or Grade 2 is mandatory.

4. Carrier Resin Compatibility
Masterbatch performance depends heavily on its carrier resin.
What to Check:
Carrier resin type (LDPE, LLDPE, PP, EVA, PS, ABS etc.)
Compatibility with your base polymer
Melt blending behavior
Why It Matters:
Wrong carrier causes:
poor bonding
migration issues
surface blooming
weak tensile properties
processing instability
Example:
Using LDPE-based masterbatch in PP injection molding can lead to:
reduced stiffness
shrinkage mismatch
warpage
poor dispersion

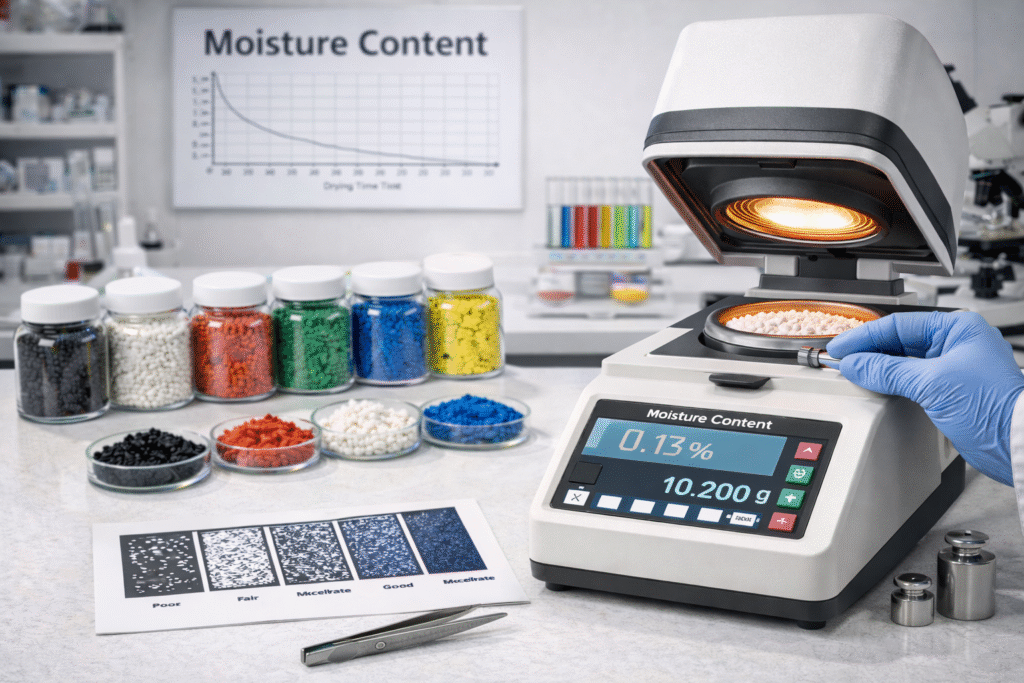
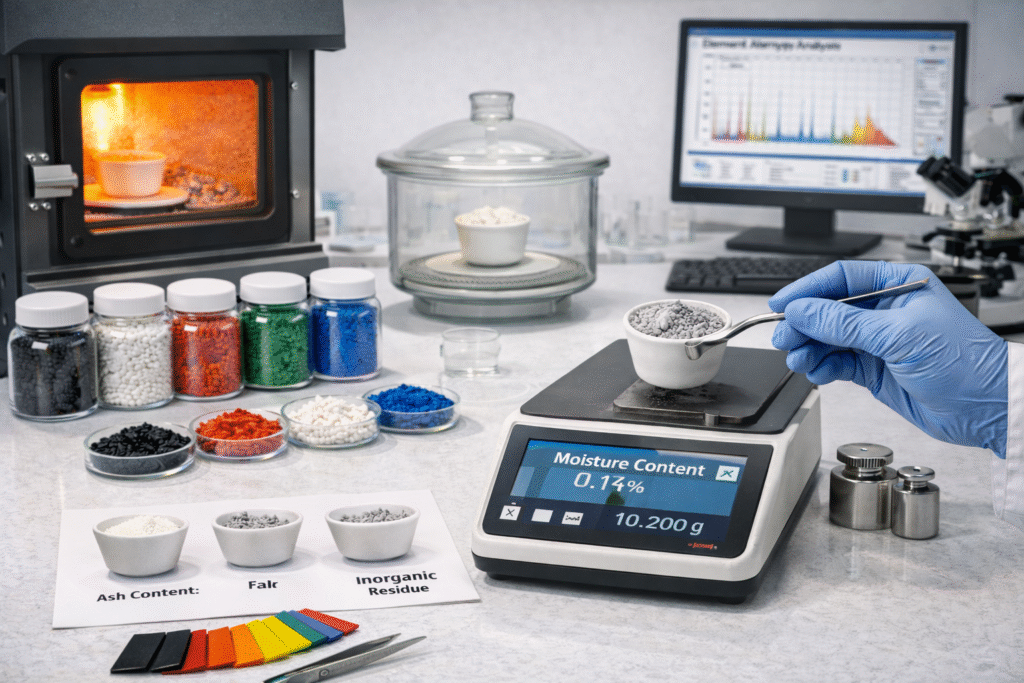
5. Moisture Content (Critical for Film & Engineering Plastics)
Moisture is a hidden defect that can destroy processing.
What to Check:
Moisture % in masterbatch (Karl Fischer test)
Storage packaging quality
Why It Matters:
High moisture leads to:
bubble formation
voids in injection molded parts
film pinholes
surface haze
hydrolytic degradation
Acceptable Range:
Standard polyolefin masterbatch: <0.1%
Engineering polymer masterbatch: <0.05%

6. Ash Content & Inorganic Residue
Moisture is a hidden defect that can destroy processing.
fillers
pigment residue
silica contamination
calcium carbonate excess
What to Check:
Ash content test (at 550°C)
Inorganic contamination %
Why It Matters:
High ash causes:
filter choking in film extrusion
die buildup
poor gloss
higher brittleness
screw and barrel wear
For high-quality masterbatch, ash content should remain stable batch-to-batch.

7. Thermal Stability (Heat Resistance During Processing)
Many pigments and additives degrade at high processing temperatures.
What to Check:
Thermal stability test report
Color shift at processing temperature
Plate-out resistance
Why It Matters:
If masterbatch is not thermally stable:
shade changes during long runs
burnt specks appear
odor generation
yellowing
Applications Where Thermal Stability is Mandatory:
blow molding
BOPP
raffia tapes
extrusion coating
automotive parts
Purchase managers must ask:
“Is the pigment stable at 250°C continuous?”

8. Particle Size Distribution (PSD) of Pigment/Additives
A key parameter affecting:
dispersion
opacity
gloss
filter life
What to Check:
D50, D90 particle size values
supplier pigment grade consistency
Why It Matters:
Larger particles cause:
streaks and non-uniform shade
reduced color strength
surface defects
poor UV resistance performance
In premium masterbatch manufacturing, pigment is micronized and stabilized for consistent PSD.

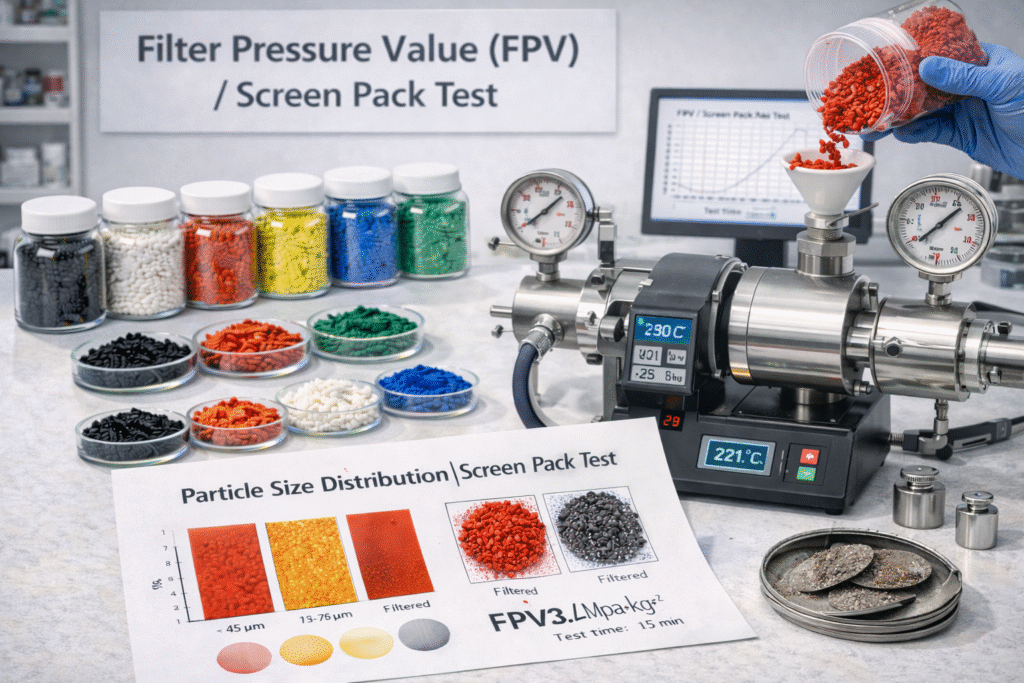
9. Filter Pressure Value (FPV) / Screen Pack Test
FPV indicates how clean the masterbatch is in terms of:
gels
carbon black lumps
unmelted particles
contamination
What to Check:
FPV test report
mesh size used (commonly 80/120/200 mesh)
Why It Matters:
High FPV means:
frequent screen change
downtime
high wastage
reduced extrusion output
For film extrusion companies, FPV is one of the most important procurement checks.
10. Color Strength & Tinting Strength
Color strength refers to how effectively the pigment colors the polymer.
What to Check:
ΔE value in lab testing
Tinting strength comparison
Spectrophotometer test report
Why It Matters:
If color strength varies:
dosing increases unexpectedly
shade mismatch in customer approval
higher consumption of masterbatch
Standard Testing:
Use spectrophotometer for:
Lab values*
ΔE measurement
reflectance curve matching
For B2B packaging and consumer goods, ΔE should ideally be:
≤ 1.0 for critical applications
≤ 1.5 for standard packaging

11. Let-Down Ratio (LDR) Consistency
Let-down ratio means how much polymer can be colored per kg of masterbatch.
What to Check:
Recommended dosing %
Real performance at customer site trials
Why It Matters:
Some suppliers claim:
LDR 1:50
But actual performance may be:
1:35
This directly increases raw material cost.
Procurement Tip:
Always conduct plant trial and validate:
actual shade match at given dosing
mechanical property retention

12. Migration / Colour Fastness
Migration occurs when additives/pigments move to the surface over time
What to Check:
Migration test report
surface blooming evaluation
compatibility with polymer
Why It Matters:
Migration causes:
surface whitening
oily layer formation
print adhesion failure
lamination issues
This is critical for:
packaging films
agricultural films
printed products
multilayer structures

13. Odor Level & VOC Content
For packaging, medical, and consumer products, odor is critical.
What to Check:
Odor evaluation report
VOC compliance if applicable
Why It Matters:
Bad odor can lead to:
rejection from food packaging buyers
customer complaints
export shipment issues
Purchase managers must verify:
low odor pigments
food-grade compliant additives

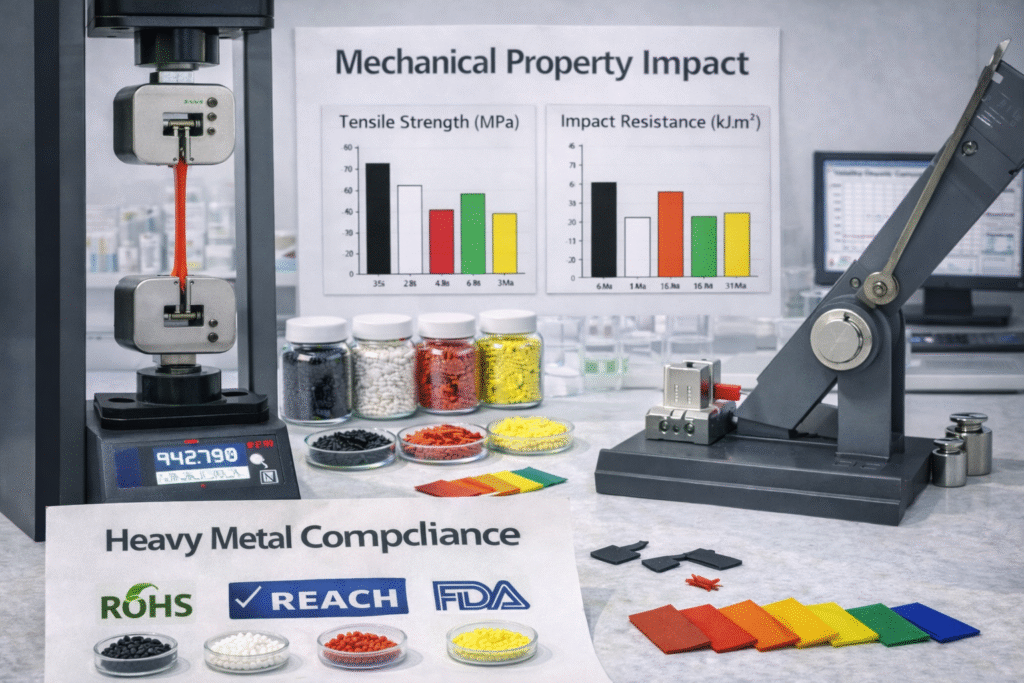
14. Heavy Metal Compliance (RoHS, REACH, FDA Requirements)
Many pigments contain traces of:
lead
cadmium
chromium
mercury
What to Check:
RoHS certificate
REACH compliance
FDA/food contact declaration (if required)
Why It Matters:
Non-compliance can lead to:
export rejection
legal penalties
loss of customer trust
Procurement should demand:
batch-wise compliance documentation

15. Mechanical Property Impact
Masterbatch must not degrade base polymer properties.
What to Check:
tensile strength retention
elongation retention
impact strength retention
Why It Matters:
Excess filler or poor carrier can reduce:
elongation in films
tear strength
ESCR (environmental stress crack resistance)
This becomes extremely important in:
stretch film
garbage bags
irrigation pipes
blow molded containers
Quality Parameters Checklist Purchase Managers Must Demand
Here is a professional checklist every procurement department should include in their vendor evaluation:
- COA (Certificate of Analysis)
- MFI report
- Dispersion rating report
- FPV/screen pack test report
- Ash content report
- Moisture content report
- Thermal stability test
- Spectrophotometer ΔE report
- Carrier resin declaration
- RoHS/REACH/FDA compliance certificates
- Batch consistency report (last 3 batches comparison)
Common Red Flags When Buying Masterbatch
If you see these warning signs, reconsider the supplier:
🚫 Supplier avoids giving COA
🚫 No batch-to-batch tracking
🚫 Shade differs in each lot
🚫 Excess dusting in granules
🚫 High contamination in packaging
🚫 Poor pellet cutting uniformity
🚫 High filter choking complaints
🚫 No lab testing setup
Best Procurement Practice: Standardize Your Masterbatch Evaluation
To reduce production risk, procurement teams should create:
Approved Masterbatch Specification Sheet
Including:
Carrier polymer
Melt flow range
Dispersion grade
Moisture max limit
Ash max limit
ΔE tolerance
letdown ratio
FPV max allowable
This ensures purchase decisions remain technical, not emotional or price-based.
Conclusion: Masterbatch Buying is a Technical Decision, Not a Commercial One
For B2B plastic processors, the cost of poor masterbatch quality is not limited to raw material—it affects:
machine performance
production output
downtime
scrap generation
customer complaints
brand reputation
A smart purchase manager evaluates masterbatch with technical parameters, documented test reports, and batch consistency assurance.
If your supplier cannot provide quality documentation, then the masterbatch is not a raw material—it becomes a production risk.
About Bajaj Plast Pvt. Ltd.
Bajaj Plast Pvt. Ltd. is a leading manufacturer of high-quality masterbatch solutions, dedicated to innovation, sustainability, and excellence. With a strong focus on customer satisfaction and cutting-edge technology, we are committed to delivering superior products that meet the evolving needs of the polymer industry.



